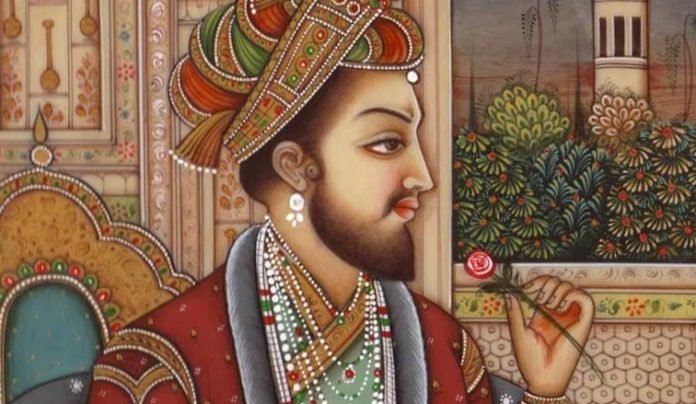
The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan was a Mughal emperor who ruled over the Indian subcontinent from 1628 until 1658. He is best known for commissioning the construction of the Taj Mahal in memory of his beloved wife Mumtaz Mahal, who died during childbirth.
The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan was born in 1592 in Lahore, in present-day Pakistan. He was the fifth Mughal emperor and was the son of the Mughal emperor Jahangir. Shah Jahan came to the throne in 1628 after a power struggle with his brothers.
you also like to read: Experience the Majesty of the Taj Mahal in One Day: A Thrilling Same Day Agra Tour by Car from Delhi
During his reign, The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan expanded the Mughal Empire and promoted art, architecture, and literature. He commissioned several magnificent buildings and monuments, such as the Taj Mahal, the Red Fort in Delhi, and the Jama Masjid in Delhi.
Shah Jahan was also known for his military campaigns and his patronage of the arts. He was a lover of poetry, music, and calligraphy, and his court was filled with artists, musicians, and scholars.
“Shah Jahan: The Magnificent Mughal Emperor Who Built the Taj Mahal and Transformed India”
Shah Jahan’s reign was marked by political turmoil and conflict with his sons. In 1658, he was overthrown by his son Aurangzeb and was imprisoned in the Agra Fort until his death in 1666.
The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan was a significant figure in Indian history and is remembered for his contributions to art, architecture, and literature. He is particularly renowned for the Taj Mahal, which is considered one of the most beautiful buildings in the world.
What was the reason for the conflict between Shah Jahan and his sons?
The conflict between Shah Jahan and his sons was mainly due to a struggle for power and succession to the Mughal throne.

Shah Jahan had four sons: Dara Shikoh, Shah Shuja, Aurangzeb, and Murad Baksh. He had initially designated his eldest son Dara Shikoh as his heir, but this decision was not accepted by his other sons.
The conflict between The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan and his sons began in 1657 when he fell seriously ill and was unable to rule effectively. His sons saw this as an opportunity to stake their claim for the throne. Aurangzeb, who was the third son, rebelled against his father and declared himself the rightful heir.
Aurangzeb’s rebellion led to a civil war between Shah Jahan and his sons, with each son vying for the throne. Dara Shikoh was initially able to gain the support of most of the Mughal nobles and defeated Shah Shuja, who had also declared himself emperor. However, Aurangzeb was able to gather support from the Deccan region and defeated Dara Shikoh in a battle in 1659.
After Aurangzeb’s victory, he imprisoned his father Shah Jahan in the Agra Fort, where he remained until his death in 1666. Aurangzeb then ascended the throne as the Mughal emperor.
The conflict between The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan and his sons was mainly due to a struggle for power and succession to the Mughal throne. Aurangzeb’s rebellion and subsequent victory led to his ascension to the throne and marked the end of the reign of the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan.
“The conflict between The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan and his sons was mainly due to a struggle for power and succession to the Mughal throne.”
What was the impact of Shah Jahan’s reign on Indian art and literature?
Shah Jahan’s reign had a significant impact on Indian art and literature. He was a patron of the arts and literature, and his reign is considered one of the high points of Mughal art and culture.
Under Shah Jahan’s patronage, Mughal art and architecture reached new heights of refinement and grandeur. He commissioned several magnificent buildings and monuments, such as the Taj Mahal, the Red Fort in Delhi, and the Jama Masjid in Delhi. The Taj Mahal, in particular, is considered one of the most beautiful buildings in the world and is a masterpiece of Mughal architecture.
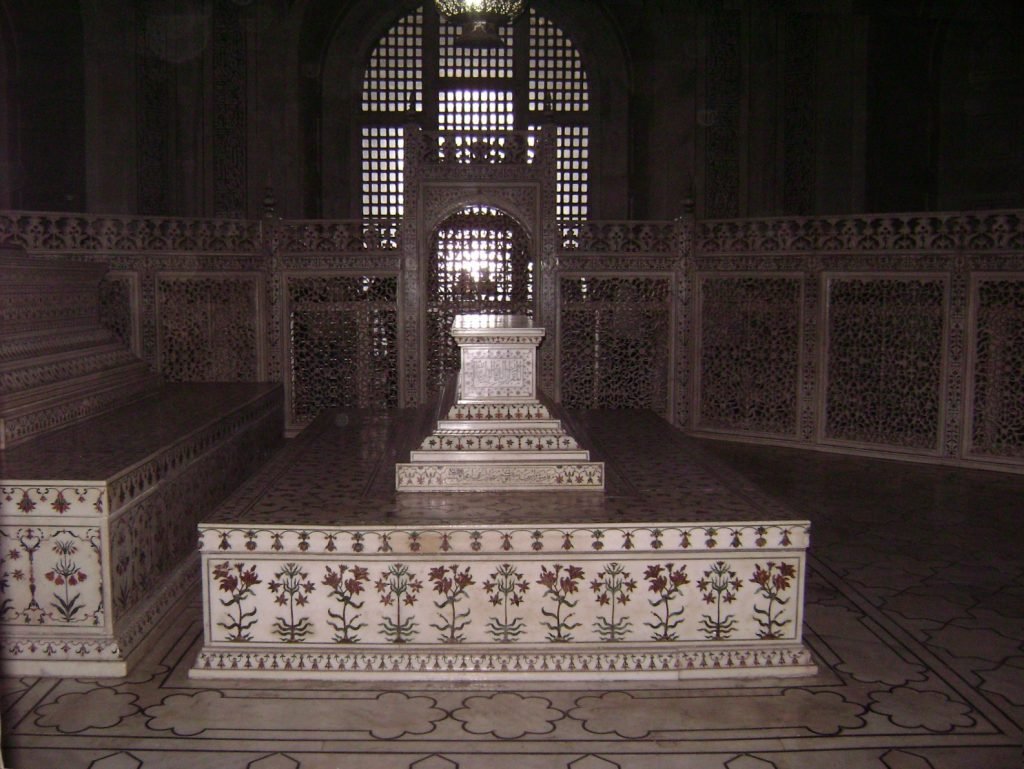
The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan also encouraged the arts of painting, calligraphy, and music. Mughal painting flourished under his patronage, with artists producing exquisite works of art in a variety of styles. Calligraphy also reached new heights of beauty and refinement, with the development of new scripts and styles.
In literature, The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan was a patron of Persian poetry and prose. He himself was a poet and wrote several works of poetry in Persian. The court of Shah Jahan was a center of literary activity, with poets and writers from all over the Islamic world gathering to exchange ideas and produce great works of literature.
“The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan also encouraged the arts of painting, calligraphy, and music.”
Shah Jahan’s reign had a profound impact on Indian art and literature. His patronage of the arts and literature led to the development of new styles and forms of expression, and his legacy continues to inspire artists and writers today.
What other significant buildings did Shah Jahan commission?
The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan was a great patron of architecture and commissioned several significant buildings and monuments during his reign. Apart from the Taj Mahal, which is his most famous commission, some of the other important buildings that he commissioned include:
Red Fort, Delhi: The Red Fort in Delhi was built by The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan in the mid-17th century as a palace for the Mughal emperor. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is one of the most important landmarks in Delhi.
Jama Masjid, Delhi: The Jama Masjid in Delhi is one of the largest mosques in India and was commissioned by The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan in the 17th century. It is a magnificent example of Mughal architecture and is one of the most famous landmarks in Delhi.

Moti Masjid, Agra: The Moti Masjid in Agra was commissioned by The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan in the 17th century and is a beautiful example of Mughal architecture. It is a small mosque made of white marble and is located inside the Agra Fort.
You also like to read: Photo of the Taj Mahal – Taj Mahal Photo Tours and The best time to visit the Taj Mahal for photography
Shalimar Bagh, Kashmir: The Shalimar Bagh in Kashmir is a beautiful garden that was commissioned by Shah Jahan in the 17th century. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is known for its stunning fountains, terraces, and pavilions.
Diwan-i-Khas, Agra Fort: The Diwan-i-Khas in the Agra Fort was commissioned by The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan in the 17th century and was used as a hall for private audiences. It is a beautiful building made of white marble and is known for its intricate carvings and decorations.
Shah Jahan’s commissions had a significant impact on Mughal architecture and continue to be important landmarks and tourist attractions in India.

































